第十四讲-现代优化算法
习题14.1(1)
1. 题目要求
假设有12件物品,质量和价值如下表所示。包的最大允许质量是46公斤。
试使用模拟退火算法和遗传算法求解包中可装载物品的最大价值。
| 物品编号 | 质量(公斤) | 价值(元) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 5 |
| 2 | 5 | 10 |
| 3 | 18 | 13 |
| 4 | 3 | 4 |
| 5 | 2 | 3 |
| 6 | 5 | 11 |
| 7 | 10 | 13 |
| 8 | 4 | 10 |
| 9 | 11 | 8 |
| 10 | 7 | 16 |
| 11 | 14 | 7 |
| 12 | 6 | 4 |
2.解题过程——模拟退火算法
解:
记12件物品的的质量和价值为 \(m_i,v_i,i=1,2,..,12\) 最大容量为 \(cnt=46\)。
(1)解空间
解空间可以写为: $$ \mathbf{S}={(\pi_1,\pi_2,...,\pi_{12})|\pi_i=0\ or\ 1,i=1,2,...,12} $$ 当 \(\pi_i=1\) 时,表示选择第 \(i\) 个物品,否则表示不选。
(2)目标函数
目标函数为最终的物品价值。我们求价值最大值,首先通过转换求价值相反数的最小值,即: $$ \min f(\pi_1,\pi_2,...,\pi_{12})=-\sum_{i=1}^{12}v_i\pi_i $$ 一次迭代由下列三步产生。
(3)新解的产生
任选序号 \(u,v,1\leq u\leq v\leq12\) ,将\(\pi_u,\pi_v\)取反,此时新的选取方法为: $$ \pi_1...\pi_{u-1}(1-\pi_u)\pi_{u+1}...\pi_{v-1}(1-\pi_v)\pi_{v+1}...\pi_{12} $$ 计算此时的重量: $$ M=\sum_{i=1}^{12}m_i\pi_i $$ 若 \(M\leq cnt\) 则新解有效,否则重新生成。
(4)代价函数差
路径差可以表示为: $$ \Delta f=-(1-\pi_u)v_u-(1-\pi_v)v_v+\pi_uv_u+\pi_vv_v $$ (5)接受准则 $$ \begin{align} P=\begin{cases} 1,&\Delta f<0\ e^{\frac{-\Delta f}{T}},&\Delta f \geq 0 \end{cases} \end{align} $$ (6)降温
选定降温系数 \(\alpha=0.999\) 降温,取新温度 \(T=\alpha T\) ,初始温度 \(T=1\)。
(7)结束条件
选定终止温度 \(e=10^{-30}\) 判断退火是否结束,当 \(T\leq e\) 时,结束模拟,输出当前状态。
3.程序
求解的MATLAB程序如下:
clc, clear
mass = [2, 5, 18, 3, 2, 5, 10, 4, 11, 7, 14, 6]; % 物品质量
value = [5, 10, 13, 4, 3, 11, 13, 10, 8, 16, 7, 4]; % 物品价值
solution = zeros(1, length(mass)); % 初始化解
max_mass = 46; % 最大允许质量
min_temperature = 0.1^30;
iterations = 20000;
alpha = 0.999;
temperature = 1;
for k = 1:iterations
old_value = -sum(solution.*value);
temp_solution = solution;
while 1
item = 1 + floor(length(mass)*rand(1, 2));
temp_solution(item) = ~temp_solution(item); % 改变选取物品的状态
if sum(temp_solution.*mass) > max_mass % 如果超过背包最大允许质量,重新选取
temp_solution = solution;
continue
else
break
end
end
new_value = -sum(temp_solution.*value);
df = new_value - old_value;
if df < 0 || exp(-df/temperature) >= rand % 接受新解
solution = temp_solution;
end
temperature = temperature * alpha; % 降温
if temperature < min_temperature
break
end
end
solution, total_mass = sum(solution.*mass), best_value = sum(solution.*value)
4.结果

得到结果为: $$ \pi_i=1,1,0,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,0,0 $$ 即选取第1,2,5,6,7,8,9,10件物品,总重量为46,价值为76。
习题14.1(2)
1. 题目要求
同上。
2.解题过程——遗传算法
解:
设定种群大小 \(M=100\) ,最大迭代次数 \(G=30\) ,交叉率 \(p_c=0.95\) ,变异率 \(p_m=0.15\) 。
基因采取编码: $$ \pi_1,\pi_2,...,\pi_{12},\pi_i=0\ or\ 1,i=1,2,..,12 $$ 使用改良圈算法产生 \(M\) 个可行解,转化为初始基因编码,目标函数为最终的物品价值即 $$ \max f(\pi_1,\pi_2,...,\pi_{12})=\sum_{i=1}^{12}v_i\pi_i $$ 接下来每一次的迭代都以概率 \(p_c,p_m\) 进行基因重组和基因变异,最后选择目标函数值最大的 \(M\) 个个体进化到下一代。
3.程序
求解的MATLAB程序如下:
clc, clear
% 输入数据
weights = [2, 5, 18, 3, 2, 5, 10, 4, 11, 7, 14, 6];
values = [5, 10, 13, 4, 3, 11, 13, 10, 8, 16, 7, 4];
num_items = length(weights);
cross_rate = .95; % 交叉概率
mutation_rate = .15; % 变异概率
max_iter = 30; % 最大迭代次数
pop_size = 100; % 种群大小
max_capacity = 46; % 背包最大承重
% 构建初始种群
population = init_population(pop_size, num_items, weights, max_capacity);
% 初始化统计指标
avg_values = zeros(1, max_iter);
max_values = zeros(1, max_iter);
% 迭代进化
for i = 1:max_iter
% 交叉
offspring_cross = crossover(population, cross_rate, weights, max_capacity);
% 变异
offspring_mutate = mutation(population, mutation_rate, weights, max_capacity);
% 选择
population = selection([population; offspring_cross; offspring_mutate], pop_size, values);
% 统计当前迭代的平均价值和最大价值
avg_values(i) = mean(sum(population*values', 2));
max_values(i) = max(sum(population*values', 2));
end
% 输出结果
best_solution = population(1, :)
best_value = sum(best_solution*values')
best_mass = sum(best_solution*weights')
% ************************* 以下为函数实现 *************************
% 初始化种群函数
function population = init_population(pop_size, num_items, weights, max_capacity)
population = zeros(pop_size, num_items);
for i = 1:pop_size
chromosome = round(rand(1, num_items));
while sum(chromosome.*weights) > max_capacity
chromosome = round(rand(1, num_items));
end
population(i, :) = chromosome;
end
end
% 交叉函数
function offspring = crossover(population, cross_rate, weights, max_capacity)
offspring = population;
num_individuals = size(population, 1);
for i = 1:2:num_individuals
if rand < cross_rate
cross_point = ceil(rand * size(population, 2));
temp1 = offspring(i, :);
temp2 = offspring(i+1, :);
temp1(cross_point) = temp2(cross_point);
temp2(cross_point) = offspring(i, cross_point);
if (temp1 * weights' <= max_capacity) && (temp2 * weights' <= max_capacity)
offspring(i, :) = temp1;
offspring(i+1, :) = temp2;
end
end
end
end
% 变异函数
function offspring = mutation(population, mutation_rate, weights, max_capacity)
offspring = population;
for i = 1:size(population, 1)
if rand < mutation_rate
mutate_point = ceil(rand * size(population, 2));
temp = offspring(i, :);
temp(mutate_point) = ~temp(mutate_point);
if sum(temp.*weights) <= max_capacity
offspring(i, :) = temp;
end
end
end
end
% 选择函数
function new_population = selection(population, pop_size, values)
fitness_values = sum(population*values', 2);
[~, sorted_indices] = sort(fitness_values, 'descend');
new_population = population(sorted_indices(1:pop_size), :);
end
4.结果
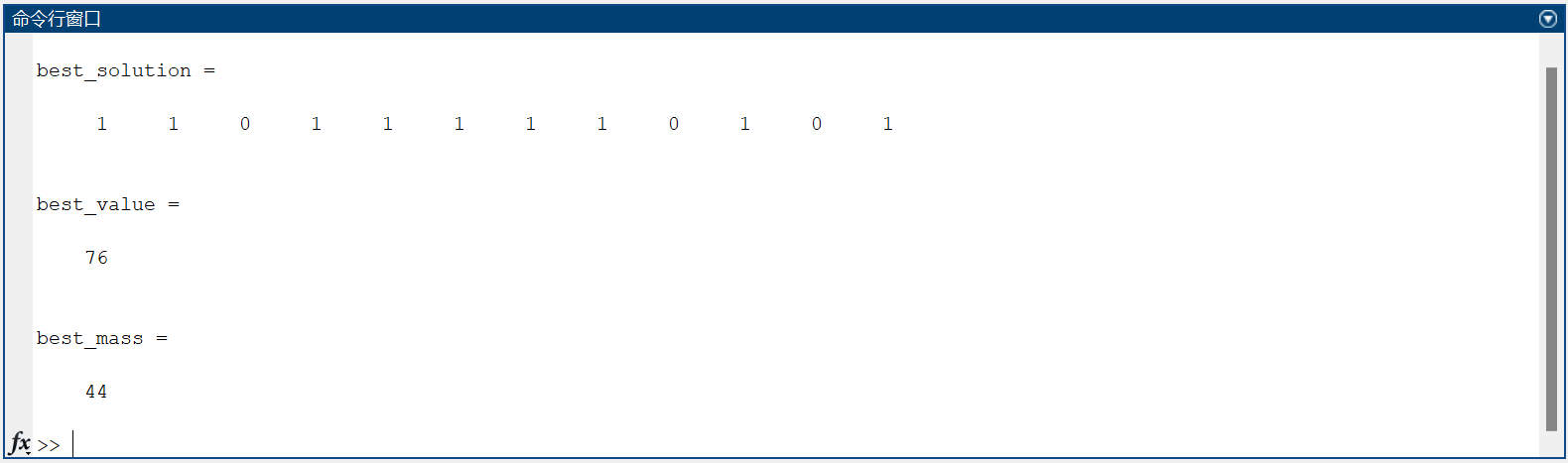
得到结果为: $$ \pi_i=1,1,0,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,0,0 $$ 即选取第1,2,5,6,7,8,9,10件物品,总重量为46,价值为76。
习题14.2(1)
1. 题目要求
假设有一个旅行商人要拜访全国 31 个省会城市,他需要选择所要走的路径,路径的限制是每个城市只能拜访一次,而且最后要回到原来出发的城市。
全国 31 个省会城市的坐标如下表所示。
试使用模拟退火算法和遗传算寻找最短路径。
| 城市编号 | 坐标(X) | 坐标(Y) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1304 | 2312 |
| 2 | 3639 | 1315 |
| 3 | 4177 | 2244 |
| 4 | 3712 | 1399 |
| 5 | 3488 | 1535 |
| 6 | 3326 | 1556 |
| 7 | 3238 | 1229 |
| 8 | 4196 | 1004 |
| 9 | 4312 | 790 |
| 10 | 4386 | 570 |
| 11 | 3007 | 1970 |
| 12 | 2562 | 1756 |
| 13 | 2788 | 1491 |
| 14 | 2381 | 1676 |
| 15 | 1332 | 695 |
| 16 | 3715 | 1678 |
| 17 | 3918 | 2179 |
| 18 | 4061 | 2370 |
| 19 | 3780 | 2212 |
| 20 | 3676 | 2578 |
| 21 | 4029 | 2838 |
| 22 | 4263 | 2931 |
| 23 | 3429 | 1908 |
| 24 | 3507 | 2367 |
| 25 | 3394 | 2643 |
| 26 | 3439 | 3201 |
| 27 | 2935 | 3240 |
| 28 | 3140 | 3550 |
| 29 | 2545 | 2357 |
| 30 | 2778 | 2826 |
| 31 | 2370 | 2975 |
2.解题过程——模拟退火算法
解:
设城市 \(i,j\) 之间的距离 \(d_{ij}=\sqrt{(x_i-x_j)^2+(y_i-y_j)^2}\) 。
(1)解空间
解空间可以表示为: $$ \mathbf{S}={(\pi_1,\pi_2,...,\pi_{31})|(\pi_1,\pi_2,...,\pi_{31})\mbox{为}{1,2,...,31}\mbox{的全排列}} $$ 特别的,规定 \(\pi_0=\pi_{31},\pi_{32}=\pi_1\)。
初始解可以选择为 \((1,2,...,31)\) 。
(2)目标函数
目标函数为路径长度: $$ \min f(\pi_1,\pi_2,...,\pi_{31})=\sum_{i=1}^{31}d_{\pi_i\pi_{i+1}} $$ 一次迭代由下列三步产生.
(3)新解的产生
任选序 \(u,v,1\leq u\leq v\leq 31\) ,交换 \(u,v\) 之间的顺序交换,此时新路径为: $$ \pi_1...\pi_{u-1}\pi_u\pi_{u+1}...\pi_{v-1}\pi_v\pi_{v+1}...\pi_{31} $$ (4)代价函数差 $$ \Delta f=d_{\pi_{u-1}\pi_v}+d_{\pi_{u}\pi_{v+1}}-d_{\pi_{u-1}\pi_{u}}-d_{\pi_{v}\pi_{v+1}} $$ (5)接受准则 $$ \begin{align*}
P=\begin{cases}
1,&\Delta f<0\\
e^{\frac{-\Delta f}{T}},&\Delta f \geq 0
\end{cases}
\end{align} $$ (6)降温*
选定降温系数 \(\alpha=0.9999\) 降温,取新温度 \(T=\alpha T\) ,初始温度 \(T=100\).
(7)结束条件
选定终止温度 \(e=10^{-30}\) ,当\(T\leq e\)时,结束模拟。
3.程序
求解的MATLAB程序如下:
clc, clear
% 城市坐标
city_coordinates = [1304, 2312; 3639, 1315; 4177, 2244; 3712, 1399; 3488, 1535; 3326, 1556; ...
3238, 1229; 4196, 1004; 4312, 790; 4386, 570; 3007, 1970; 2562, 1756; ...
2788, 1491; 2381, 1676; 1332, 695; 3715, 1678; 3918, 2179; 4061, 2370; ...
3780, 2212; 3676, 2578; 4029, 2838; 4263, 2931; 3429, 1908; 3507, 2367; ...
3394, 2643; 3439, 3201; 2935, 3240; 3140, 3550; 2545, 2357; 2778, 2826; ...
2370, 2975];
num_cities = size(city_coordinates, 1);
% 初始化路径
path = 1:num_cities;
% 计算距离矩阵
distances = pdist2(city_coordinates, city_coordinates);
% 初始化总距离
total_distance = sum(distances(sub2ind(size(distances), path, [path(2:end), path(1)])));
% 设置退火参数
initial_temperature = 100;
alpha = 0.9999;
final_temperature = 0.1^30;
temperature = initial_temperature;
while temperature > final_temperature
% 随机选择两个城市
cities_to_swap = sort(randperm(num_cities, 2));
% 生成新路径
new_path = path;
new_path(cities_to_swap(1):cities_to_swap(2)) = new_path(cities_to_swap(2):-1:cities_to_swap(1));
% 计算新距离
new_distance = sum(distances(sub2ind(size(distances), new_path, [new_path(2:end), new_path(1)])));
% 判断是否接受新解
if new_distance < total_distance || rand < exp((total_distance - new_distance) / temperature)
path = new_path;
total_distance = new_distance;
end
% 降温
temperature = temperature * alpha;
end
% 输出结果
disp('Optimal path:');
disp(path);
disp('Total distance:');
disp(total_distance);
% 绘制图像
plot(city_coordinates([path, path(1)], 1), city_coordinates([path, path(1)], 2), '-o');
4.结果

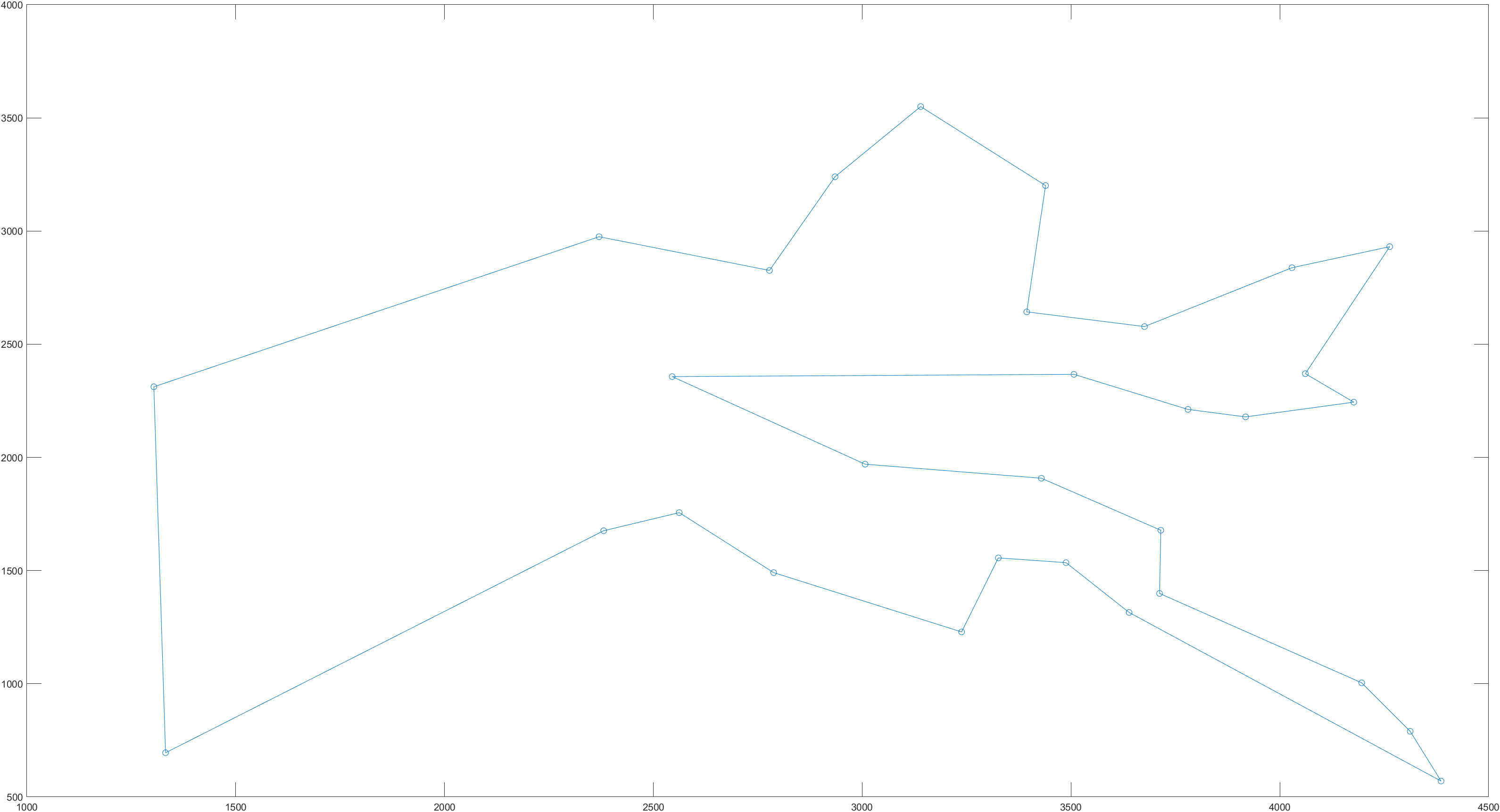
最终得到的结果如图,路径长度 \(D=15437\)。
习题14.2(2)
1. 题目要求
同上。
2.解题过程
解:
设定种群大小 \(M=100\) ,最大迭代次数 \(G=100\)。
交叉率 \(p_c=1\)。
变异率 \(p_m=0.15\) 。
基因编码用随机数列 \(\omega_1\omega_2...\omega_{31},0\leq\omega_i\leq1\) 其中 \(\omega_i\) 在整个序列中的升序排序位置为城市 \(i\) 所在的位置。
使用改良圈算法产生\(M\)个可行解,转化为初始基因编码,目标函数为最终的物品价值即: $$ \max f(\pi_1,\pi_2,...,\pi_{12})=\sum_{i=1}^{12}v_i\pi_i $$ 接下来每一次的迭代都以概率 \(p_c,p_m\) 进行基因重组和基因变异,最后选择目标函数值最大的 \(M\) 个个体进化到下一代。
3.程序——遗传算法
求解的MATLAB程序如下:
clc, clear
distanceMatrix = zeros(31);
optimalPath = zeros(1, 31);
coordinates = [1304, 2312; 3639, 1315; 4177, 2244; 3712, 1399; 3488, 1535; 3326, 1556; ...
3238, 1229; 4196, 1004; 4312, 790; 4386, 570; 3007, 1970; 2562, 1756; ...
2788, 1491; 2381, 1676; 1332, 695; 3715, 1678; 3918, 2179; 4061, 2370; ...
3780, 2212; 3676, 2578; 4029, 2838; 4263, 2931; 3429, 1908; 3507, 2367; ...
3394, 2643; 3439, 3201; 2935, 3240; 3140, 3550; 2545, 2357; 2778, 2826; ...
2370, 2975];
for i = 1:31
optimalPath(i) = i;
for j = 1:31
distanceMatrix(i, j) = sqrt((coordinates(i, 1) - coordinates(j, 1))^2+(coordinates(i, 2) - coordinates(j, 2))^2);
end
end
distance = 0;
for i = 1:30
distance = distance + distanceMatrix(optimalPath(i), optimalPath(i+1));
end
distance = distance + distanceMatrix(optimalPath(1), optimalPath(31));
w = 100;
g = 100;
rand('state', sum(clock)); % 初始化随机数发生器
for k = 1:w % 通过改良圈算法选取初始种群
c1 = randperm(31); % 产生1,..,31的一个全排列
for t = 1:100 % 该层循环是修改圈
flag = 0; % 修改圈退出标志
for m = 1:31
for n = m + 1:31
m1 = m - 1;
n1 = n + 1;
if m == 1 && n == 31
continue
end
if m1 == 0
m1 = 31;
end
if n1 == 32
n1 = 1;
end
if distanceMatrix(c1(m1), c1(n)) + distanceMatrix(c1(m), c1(n1)) < ...
distanceMatrix(c1(m), c1(m1)) + distanceMatrix(c1(n), c1(n1))
c1 = [c1(1:m-1), c1(n:-1:m), c1(n+1:31)];
flag = 1; % 修改圈
end
end
end
if flag == 0
chromosomeMatrix(k, c1) = 1:31;
break % 记录下较好的解并退出当前层循环
end
end
end
chromosomeMatrix(:, 1) = 0;
chromosomeMatrix = chromosomeMatrix / 31; % 把整数序列转换成[0,1]区间上的实数,即转换成染色体编码
for k = 1:g % 该层循环进行遗传算法的操作
childPopulation = chromosomeMatrix; % 交配产生子代 A 的初始染色体
c = randperm(w); % 产生下面交叉操作的染色体对
for i = 1:2:w
F = 1 + floor(31*rand(1)); % 产生交叉操作的地址
temp = childPopulation(c(i), [F:31]); % 中间变量的保存值
childPopulation(c(i), [F:31]) = childPopulation(c(i+1), [F:31]); % 交叉操作
childPopulation(c(i+1), F:31) = temp;
end
by = []; % 为了防止下面产生空地址,这里先初始化
while ~length(by)
by = find(rand(1, w) < 0.15); % 产生变异操作的地址
end
mutationList = childPopulation(by, :); % 产生变异操作的初始染色体
for j = 1:length(by)
bw = sort(1+floor(31*rand(1, 3))); % 产生变异操作的3个地址
mutationList(j, :) = mutationList(j, [1:bw(1) - 1, bw(2) + 1:bw(3), bw(1):bw(2), bw(3) + 1:31]); % 交换位置
end
G = [chromosomeMatrix; childPopulation; mutationList]; % 父代和子代种群合在一起
[SG, indl] = sort(G, 2);
populationSize = size(G, 1);
pathLengths = zeros(1, populationSize); % 路径长度的初始值
for j = 1:populationSize
for i = 1:31
if i == 31
pathLengths(j) = pathLengths(j) + distanceMatrix(indl(j, i), indl(j, 1));
else
pathLengths(j) = pathLengths(j) + distanceMatrix(indl(j, i), indl(j, i+1)); % 计算每条路径长度
end
end
end
[slong, ind2] = sort(pathLengths); % 对路径长度从小到大排序
chromosomeMatrix = G(ind2(1:w), :); % 精选前 w 个较短的路径对应的染色体
end
optimalPath = indl(ind2(1), :), optimalPathLength = slong(1)
plot([coordinates(optimalPath, 1); coordinates(optimalPath(1), 1)], [coordinates(optimalPath, 2); coordinates(optimalPath(1), 2)], '- o')
4.结果


最终得到的结果如图,路径长度 \(D=15437\)。